Listen and follow
Introduction
What is Brand, Secrets Revealed, part II – Brand Connections.
In Part I, we pulled back the curtain on the mystery of branding, revealing that it’s not your logo, color scheme, or website design. A brand lives in the customer’s subconscious as neural “Connections” to all the feel-good experiences they’ve had with the brand.
We are not always aware of these memories, but nevertheless, they are very active in influencing our cognitive decision making.
In this article, we delve even deeper, giving you more insight to help you market your products with a Brand Advantage.
Need a refresher? – “What is Brand? Secrets Revealed Part I”
Connections do not have the same impact.
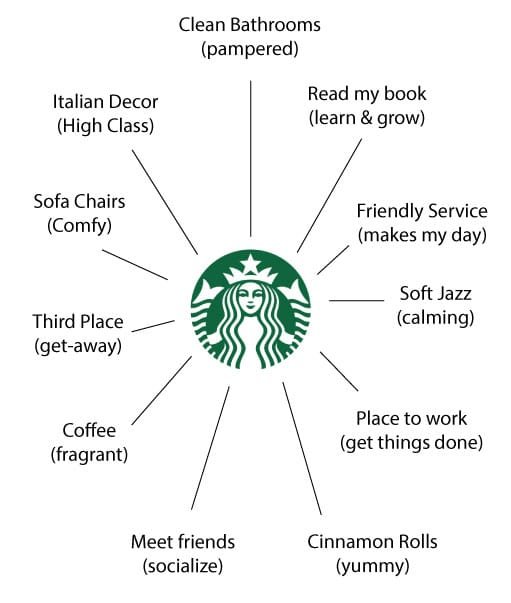
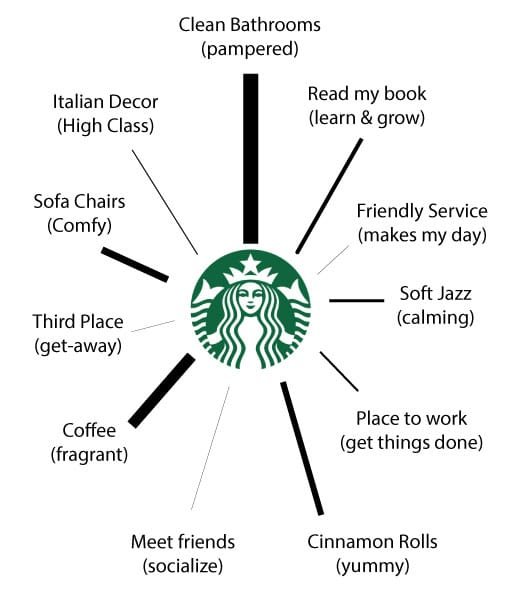
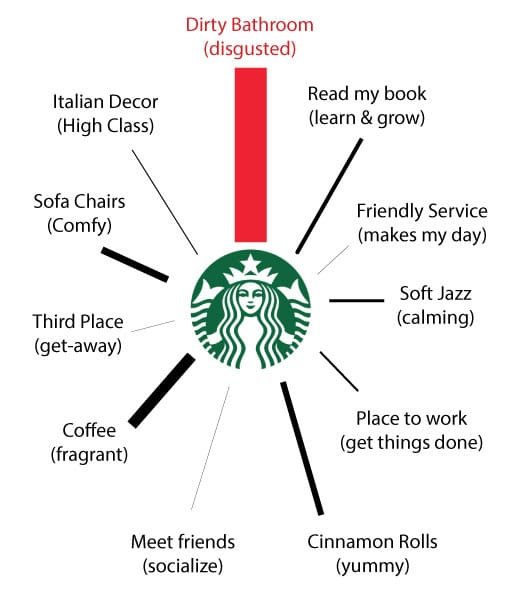
What we didn’t say in Part I is that those connections do not carry the same neural weight (Figure 2). For some, the inspiration of décor is important. For others it’s the taste of the cinnamon rolls. For me, it’s the safety of clean bathrooms. This becomes important when the experiences turn bad.
Connections to bad experiences are Brand killers
Your brand’s physical connections to your customer are also called Touchpoints. Cinnamon Rolls, Bathrooms, Coffee, Advertising, Music, and Décor can all be considered good Touchpoints.
What if you had a bad experience at any of the touchpoints – product returns, poor customer service, or even dirty bathrooms. These are accentuated several fold – It’s something we call Negative Bias, a tendency to focus on the negative more than the positive.
Negative connections can carry more weight and can impact whether they choose your brand or not. That’s why companies take great care to maintain the integrity of all Touchpoints.
Connections influence Intuitive Decision Making
In Daniel Kahneman’s book “Thinking Fast and Slow”, he differentiates how we make decisions.
- System 1 – Fast, irrational, instinctive decisions based on emotions
- System 2 – Slow, rational, deliberate decisions based on research and facts
For better or worse, irrational decision making far exceeds the rational ones. It is convenient, efficient and uses less energy.

Fig. 4 – Irrational and Rational Behavior
Irrational decisions are influenced by the neural connections and memories in our subconscious, encouraging us to make those gut feel or impulsive purchasing choices.
This is why companies should nurture these Brand Connections, to summon an instinctive, automatic decision to use your products or services. That is the ultimate advantage of a Brand.
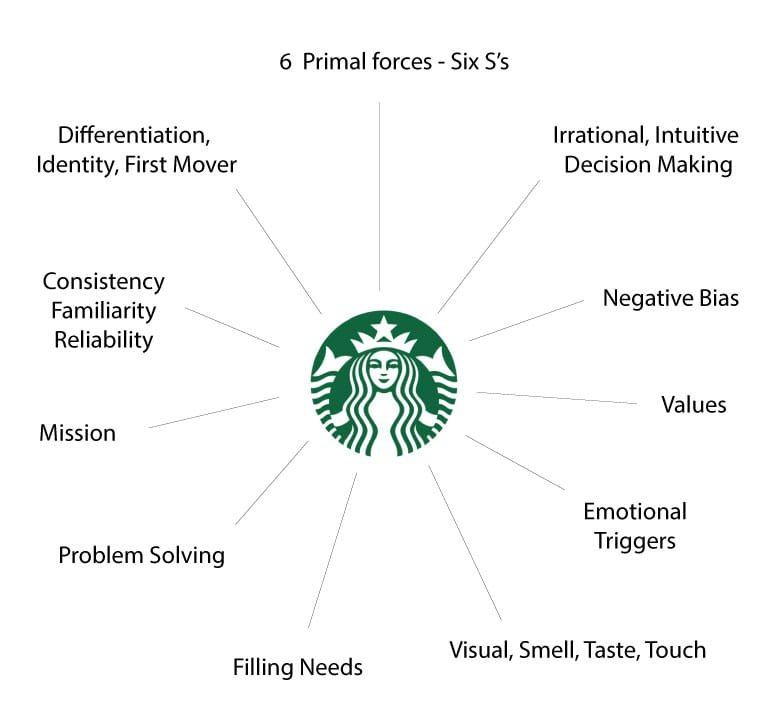
The 6 Primal Forces drive connections.
In another book “Unconscious Branding”, Douglas Van Praet notes the six “S”s that describe the biological and emotional needs of humans.
- Safety
- Security
- Sustenance
- Sex
- Status
- Survival
These are all primitive, instinctive forces of evolution that drive human behavior, and allowed our primitive ancestors to survive and thrive.

Fig. 5 – Six Primal Forces
They are also impactful as part of brand experiences. We can see this with someone walking into an meeting with a Starbucks cup as a status symbol, compared to everyone else who has convenience store coffees at half the price.
| S-term | Instinctual Drive | Example Brand Cue or Behavior |
| Safety | Avoiding threat or risk | Red Wing Shoes - Durable footwear for hazardous environments |
| Security | Seeking stability and control | Wells Fargo — trusted banking for your money |
| Sustenance | Fulfilling physical or emotional nourishment | Unilever focus on sustainable nutrition |
| Sex | Appealing to attraction or desire | Victoria Secrets - lingerie for women |
| Status | Asserting social dominance | Mercedes, Rolex and Starbucks |
| Survival | Urgency, resilience, continuity | Swiss Army Knife - all purpose tool for the outdoors |
Emotional triggers strengthen connections.
We already talked about how connections to experiences are strengthened with emotional responses. In Figure 6, we list some other emotional triggers that can be used in branding.
For example, Starbucks baristas will write your name on a cup, and call you by name when your coffee is ready – a feeling of “belonging”.
Also, emotional triggers don’t always have to be positive, as our brains are stimulated by them good or bad. For example, sadness associated with nostalgia can be used as a powerful emotional trigger.
Emotional Triggers
- belonging
- nostalgia
- confidence
- inspiration
- courage
- empathy
- fear
- sadness
- hope
- joy
- trust
- pride
- achievement
- surprise
- anger
- love
- anticipation
- and more
Fig. 6 – Emotional Triggers
Connecting with Values.
We also connect with and purchase brands from companies who share similar values
- Patagonia – Conservation, Earth-friendly, Sustainable Materials
- Tom’s Shoes – One for one – Buy a pair, donate a pair to needy children
- Warby Parker Glasses – Buy a pair, donate a pair
- Starbucks – Ethically sourced coffee from sustainable coffee organizations.
In the case of Tom’s shoes, they made their fortunes simply because of their philanthropic, empathetic Brand – as did Warby Parker Glasses.


Solving Problems, Filling Needs builds solid connections.
Anytime you can solve a problem, or fill a need for a customer, it’s a powerful emotional trigger, invoking confidence and trust with your brand, in addition to experiencing a sense of “achievement”.
As obvious as this concept may sound, it’s easy to lose this focus.
Marketers will list features and specs, trying to persuade customers to buy product. On the other hand, “Brand” Marketers use the Brand Story strategy – in short, they don’t really sell products, they solve problems.
Learn more -“What is Brand Story“
Consistency – Familiarity Is a Strong Brand Connector
“There’s no place like home.” Brands that feel familiar trigger emotional comfort and build trust.
Starbucks excels here:
- Store Layout: Whether in Seattle or Singapore, the store layout feels familiar — warm lighting, curved counters, cozy corners.
- Menu Uniformity: Customers know their go-to drink will taste the same, every time.
- Brand Voice: From signage to app notifications, the tone is friendly, human, and inviting.
Consistency cultivates brand reliability — a subtle but powerful signal that says: “We’re always here for you.”
Differentiation and Identity
While consistency builds comfort, differentiation makes you memorable – this is called Brand Identity. There are many ways to set your brand apart; product features, product quality, customer service, warranty etc.
However, as most products mature and reach commodity status, it’s hard to differentiate yourself from the other brands, and the intangibles become more important.
As we mentioned, Tom’s Shoes donated a pair of shoes for needy children for every shoe sold. That’s what set them apart as an empathetic, caring shoe seller – and even if 100 shoe companies followed suit, Tom’s would still enjoy the status of a First Mover brand.
Starbucks had been a First Mover of the “Coffee Experience”, a third place where you can meet friends, read a book, and even get some work done.

Fig. 7 – Starbucks Identity
The 4 Senses – Immersive Brand Experience
Brands speak louder when they stimulate our four senses. Starbucks orchestrates an almost theatrical experience:
| Sense | Starbucks Application |
|---|---|
| Sight | Italian-inspired décor, warm tones |
| Smell | Signature coffee roast aroma |
| Taste | Flavored drinks, pastries, seasonal blends |
| Sound | Soft jazz, espresso machines’ humming away |
This multisensory strategy turns a cup of coffee into a coffee experience. And that buys more connections.

Mission Statement – The Soul of Your Brand
Your mission statement is the brand’s north star – it sets the tone for the culture of a company, it’s characteristics, behaviors, and values – this is the point where Brand Alignment cascades from, and guides staff in their daily work.
It’s not something they think about everyday, but it’s tucked into their subconscious just like Brand Connections, and it influences their decisions and actions in their work.
Starbucks’ mission:
“To inspire and nurture the human spirit — one person, one cup, and one neighborhood at a time.”
Why it works:
- Emotionally resonant: Focuses on human connection, not just caffeine.
- Universally applicable: Relevant whether you’re serving a student, a traveler, or a business exec.
- Actionable: It guides everything from hiring practices to store ambiance.

Fig. 9 – Mission – Nurture the Spirit
Brand Strategy – Establishing Brand Connections.
As you’ve seen, there are many ways to build those neural brand connections in the customer’s subconscious mind. You’ll find that there are some overlap between the connection concepts we presented, but it should give you a good framework to start on your Brand Strategy.
And make sure you have a solid Mission Statement before anything else – it will set the tone and give you perspective as you build your brand.
Below, we summarize the Starbucks Brand Strategy.
Starbucks Brand Strategy
| Solid Mission Statement | Nurture the Human Spirit, a person, a cup, a community at a time. |
| Consistency/Familiarity | No matter San Francisco, Singapore, customers know they'll get familar experience. |
| Stimulate 4 senses | Visual (Italian Decor), Taste (cinnamon rolls), Sounds (soft jazz), Smell (roasted coffee, fresh bathrooms) |
| Emotional Triggers | Belonging, relaxation, self-improvement |
| Filling needs | Get away from home / office (third place), solitude and peacefullness |
| Values | Ethically sourced coffees |
| 6 Primal Needs | Status, Sustenance (food & emotional), Safety (clean bathrooms) |
| Differentiation / Brand Identity | Starbucks not only serves coffee, it gives customer a whole new coffee experience - nuture the Human Spirit. |
Conclusion – The secrets to Branding
We reviewed from Part I that brand is all the neural connections to the feel good experiences and memories. They live in our subconscious and influence a go or no-go decision to use our product or service.
In this Part II we explain that all those connections are part of the instinctive, spontaneous decisions to choose a brand, which is the ultimate goal of branding.
Then we detailed all the aspects of establishing those connections; touchpoints, negative bias, 6 Primal Forces, 4 Senses, Emotional Triggers, Differentiation etc.
This understanding of building connections gives Brand Marketers a good framework to start establishing a Brand Strategy.

References:
The Brand Gap – How to Bridge the Distance Between Business Strategy and Design – Marty Neumeier (Copyright 2006)
The Power of Instinct – The New Rules of Persuasion in Business and Life – Leslie Zane (Copyright 2024)
Subliminal – HowYour Unconscious Mind Rules Behavior – Leanard Mlodinow (Feb 12, 2017)
If you are looking to boost your Brand and Marketing efforts please contact us.






0 Comments